When faced with a cardiac emergency, knowing how to perform CPR can be a lifesaver. This article covers the fundamental steps and essential actions required to perform CPR effectively. Learn the key techniques and vital information you need to handle an emergency with confidence and precision.
Assess the Situation
Before you approach the victim, it’s crucial to assess the environment to ensure it’s safe for both you and the individual in need of assistance. Look for any potential hazards such as traffic, fire, or unstable structures that could pose additional risks. Ensuring the area is secure helps prevent further injury and allows you to focus on providing help effectively.
Once you’ve confirmed that the scene is safe, evaluate the victim’s condition from a distance. Check for any immediate dangers that could affect their health, such as exposure to hazardous substances. If the victim is unresponsive, you’ll need to act quickly, so be prepared to take the next steps in the CPR process while keeping the overall situation in mind.
Check Responsiveness
To determine if the victim is responsive, follow these steps:
- Gently Shake the Victim: Carefully shake the victim’s shoulders while speaking loudly to them. Use clear, assertive language such as, “Are you okay?” This action helps to gauge if the person is conscious and aware of their surroundings.
- Shout and Ask Questions: If shaking doesn’t yield a response, shout loudly and ask questions to see if there’s any reaction. For example, you might say, “Can you hear me?” or “What’s your name?” Observe if the victim shows any signs of waking or responding to your voice.
If the victim remains unresponsive after these actions, it indicates an emergency situation where immediate medical intervention is necessary. Proceed by calling for emergency help and preparing to administer CPR if required.
Call for Help
Once you’ve determined that the victim is unresponsive, it’s crucial to call for emergency assistance immediately. Use a phone to contact emergency services, and provide clear, concise information about the situation. This includes details such as the location of the incident, the nature of the emergency, and any visible symptoms or conditions of the victim. Staying calm and focused while speaking to the dispatcher will ensure that they can send help as quickly as possible.
While waiting for emergency responders to arrive, continue to monitor the victim’s condition and perform CPR if needed. It’s important to remain on the line with the dispatcher if instructed, as they may provide additional guidance or instructions based on the victim’s condition and the specifics of the emergency. Your ability to effectively communicate and follow instructions can make a significant difference in the outcome of the situation.
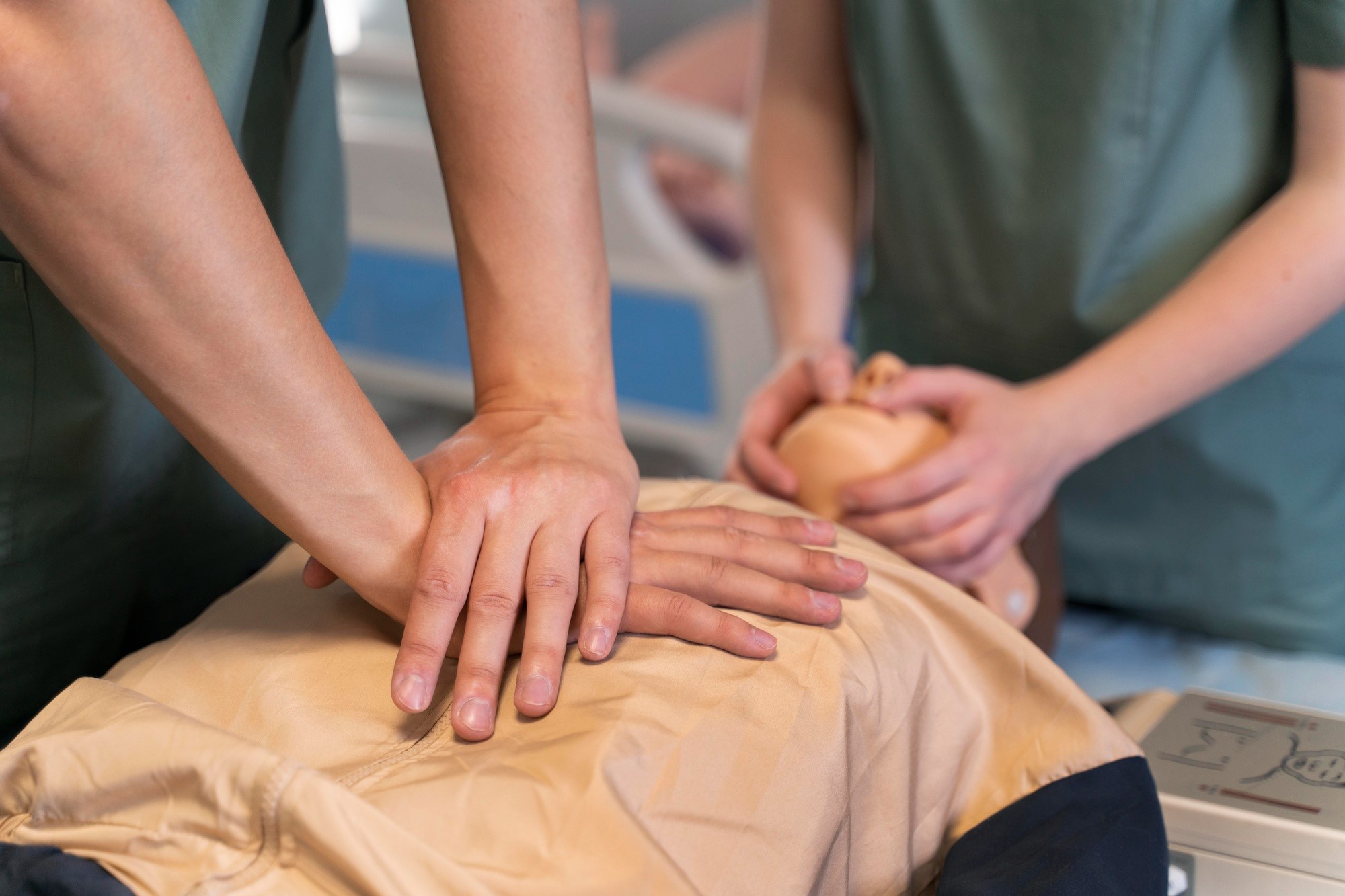
Perform Chest Compressions
To perform chest compressions effectively, follow these steps:
- Position Your Hands: Place the heel of one hand on the center of the victim’s chest, right between the nipples. Place your other hand on top of the first hand and interlock your fingers. Ensure that your arms are straight and your shoulders are directly above your hands to apply sufficient pressure.
- Begin Compressions: Use your body weight to compress the chest downwards at a depth of about 2 inches (5 cm). Maintain a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute, allowing the chest to fully recoil between compressions. This rhythmic compressing helps circulate blood to vital organs.
- Monitor Your Technique: Check that you are performing compressions at the correct depth and rate by keeping a steady rhythm. If you notice any signs of the victim regaining consciousness or movement, pause compressions briefly and reassess their condition.
Effective chest compressions are crucial for maintaining blood flow and oxygen to the victim’s brain and heart until professional medical help arrives. Continue performing compressions without interruption, especially if you are alone and cannot call for additional assistance immediately.
Give Rescue Breaths
To administer rescue breaths correctly, follow these steps:
- Open the Airway: First, ensure the victim’s airway is open by tilting their head back slightly and lifting their chin. This maneuver helps to clear the airway and allows for effective breathing. Place one hand on the victim’s forehead and use your other hand to lift the chin.
- Check for Breathing: Before giving rescue breaths, quickly check if the victim is breathing normally. Look for chest rise, listen for breath sounds, and feel for breath on your cheek. If the victim is not breathing or only gasping, proceed with rescue breaths.
- Give the Breaths: Pinch the victim’s nose shut and cover their mouth with yours, creating a tight seal. Give a breath that lasts about 1 second and make the chest rise visibly. Administer 2 rescue breaths after every 30 chest compressions. Ensure each breath is effective by observing the rise and fall of the chest.
Properly timed and effective rescue breaths are essential for providing oxygen to the victim’s lungs and maintaining adequate oxygen levels in their bloodstream. Continue with this cycle of compressions and breaths until professional help arrives or the victim shows signs of recovery.
Use an AED (Automated External Defibrillator)
| Step | Action | Purpose |
| 1. Locate AED | Find an AED device, which is often located in public places such as airports, schools, and shopping malls. | Ensures immediate access to the device in an emergency. |
| 2. Turn On AED | Press the power button to activate the AED. Follow the audible and visual prompts provided by the device. | Ensures the AED is operational and ready to use. |
| 3. Attach Pads | Place the AED electrode pads on the victim’s bare chest as indicated by the diagrams on the pads. Ensure proper placement for effective analysis. | Allows the AED to analyze the heart rhythm accurately. |
- Turn On the AED: Power on the AED by pressing the button, and follow the prompts provided by the device. The AED will guide you through each step with audio and visual instructions. Ensure you listen carefully and follow the directions precisely.
- Attach the Electrodes: Remove the victim’s clothing to expose their chest, and apply the electrode pads as indicated by the diagrams on the pads. One pad should be placed on the upper right side of the chest, and the other on the lower left side, below the armpit. This positioning helps the AED detect the heart’s electrical activity effectively.
- Analyze the Heart Rhythm: Once the pads are attached, the AED will analyze the heart’s rhythm to determine if a shock is needed. Ensure no one is touching the victim during this analysis to avoid interference. The device will indicate whether a shock is required or if CPR should continue.
- Deliver a Shock (If Advised): If the AED determines that a shock is necessary, it will instruct you to press the shock button. Make sure to stand clear of the victim during this process. The shock helps to restore a normal heart rhythm in cases of cardiac arrest.
- Continue CPR: After delivering the shock or if no shock is advised, continue with CPR as instructed by the AED. The device may prompt you to perform additional cycles of chest compressions and rescue breaths until help arrives or the victim shows signs of recovery.
Using an AED is a critical step in managing a cardiac emergency. The device is designed to be user-friendly, providing step-by-step instructions to assist you through the process. By following these instructions and integrating AED use with continuous CPR, you significantly enhance the chances of the victim’s survival and recovery.